Boothless Audiometry Provides Highly Repeatable Results for Various Tests of Auditory Performance in the Field Environment
What is Boothless Audiometry?
Almost half of all adults with noise-related hearing loss work in noisy environments.
In the U.S., approximately 37.5 million adults over the age of 18 suffer from hearing loss, including more than half of those over the age of 75. Studies have found that hearing loss and tinnitus are the most common service-connected disabilities in veterans.
Boothless audiometry is a branch of audiometry that allows audiologists to conduct a traditional sound test without the use of a sound booth. WAHTS accomplishes this by providing attenuation on par with a single-walled sound booth, and allows occupational health providers to deliver comprehensive hearing health services, on-site, in less than ideal conditions.
The use of this technology allows audiologists to administer a hearing test without the traditional booth, making it a more efficient method of audiometry with the added advantage of portability.
What is a Field Assessment?
Traditional workforce hearing assessments require travel for employees to an alternate location, disrupting work and adding to employee burden.
Boothless Audiometry allows occupational health operators the ability to provide on-site hearing healthcare including hearing testing and hearing protection fit testing, reducing or eliminating unnecessary offsite follow-ups.
As a Boothless Audiometry solution, WHATS enables occupational hearing testing in non-clinical audiology settings, such as military deployed environments, active construction sites, break rooms, and field offices.
Accurate and reliable testing at the worksite requires mitigating potential interference from background noise, which would otherwise invalidate test results. Due to the high passive attenuation of the WAHTS headset, we are able to provide accurate and valid testing in field environments.
How do you Evaluate Boothless Audiometry Devices for Field Assessments?
When selecting a Boothless Audiometry device for a field assessment, consider the following factors:
- Attenuation
Attenuation refers to the reduction of external sound received by a listener as a result of the characteristics of the headphone (e.g. how much external sound is blocked because of the headphone). This is an important feature for boothless hearing testing where ambient room noise can interfere with the accuracy of hearing testing.
Headphones with high attenuation values allow for accurate hearing testing in high noise environments because they block more ambient room noise. As can be seen in the figure below, the WAHTS earcups attenuate sound on par with a single-walled sound booth (dark blue line vs. red line). The WAHTS provides significantly more low frequency attenuation than the RadioEar DD450 (dark blue line vs. light blue line). This is important because ambient room noise tends to be low frequency in energy. The WAHTS can be used in higher noise environments than the Radio Ear DD450.
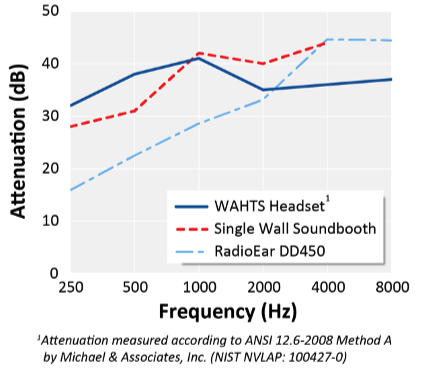
- Passive vs Active Attenuation
WAHTS does not use active noise reduction in the headset. Our system relies on high passive attenuation which refers to the ability of a headset to minimize ambient noise without requiring assistance from other electronics. The passive attenuation of the WAHTS headset is approximately 30-40 dB.
- MPANLS (Maximum Permissible Ambient Noise Levels)
OSHA specifies MPANLs for occupational hearing testing (black line in figure below). These are room noise levels which cannot be exceeded for occupational hearing testing. Recently published OSHA letter of interpretation allows for the use of ANSI-derived MPANLS which take into account the attenuation of the headset. In the figure below, the outdated OSHA MPANLs are plotted against the ANSI S3.1-1999 MPANLs. As can be seen in the figure, the WAHTS (ANSI-derived MPANLs) allows for higher room noise in the low frequencies 250-1000 Hz. This means that WAHTS can be used for accurate hearing testing in higher noise areas than any other system!
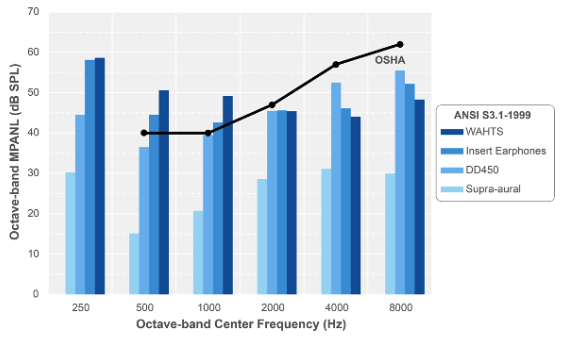
Assessing Improvements in Audiological Equipment that Encourage Boothless Audiometry
A team of research audiologists performed a Field Assessment at Marine Corps Base Camp Pendleton using WAHTS boothless audiometry to assess the auditory performance of military instructors (Kulinski et al., 2023).
The purpose of this study was to evaluate auditory performance of military instructors as part of a training course involving noise and blast exposure. Boothless audiometry was used to estimate the test-retest reliability of the auditory measures under realistic field conditions and to determine risk of acute auditory injury during standard training practices.
Thirteen U.S. Marine instructors participated in study activities. An audiologic testing battery embedded in WAHTS headset was used to test various tone detection tasks on subjects after exposure, and acoustic exposures were captured with sound level meters.
The team found that boothless audiometry provides highly repeatable results for various tests of auditory performance in the field environment. In this test population, changes in auditory performance pre- and post-noise exposure were minimal for most measures. The notable exception was binaural (NoSπ) tone detection, which showed significant degradations both as a function of pre- and post-noise exposure on the same day and as a result of cumulative noise exposure over the period of the study.
Conclusion: Benefits of Boothless Audiometry for Preserving Hearing Health
Because of its portability and durability, the WAHTS headset is ideal for auditory assessment in field environments. The high passive attenuation of the headset allows the system to be used for accurate and valid hearing testing in high noise environments outside of a sound proof booth. The WAHTS system can be used closer to the site of auditory injury, therefore helping to identify early changes in hearing in hopes of preserving overall hearing health (Barr et al., 2021 and Lee et al., 2020).
—
References:
Barr L. Mobile hearing test system enables quicker diagnosis, treatment. The official website of the Military Health System. https://health.mil/News/Artic…-diagnosis-treatment. Published July 8, 2021. Accessed June 16, 2022
Brungart D, Schurman J, Konrad-Martin D, Watts K, Buckey J, Clavier O, Jacobs P, Gordon S, Dille M. Using tablet-based technology to deliver time-efficient ototoxicity monitoring. Int J Audiol. 2018; 57(SUP4):78-86.
Devon Kulinski, Coral Dirks, Walter Carr, Benjamin Sheffield, Gary Kamimori & Douglas S. Brungart (2023) Field assessment of acute auditory responses to environmental exposures in close quarters tactics training, International Journal of Audiology, 62:2, 138-150, DOI: 10.1080/14992027.2022.2028023
Lee J, Bowley D, Miles J, Muzaffar J, Poole R, Orr L. The Downrange Acoustic Toolbox: An Active Solution for Combat-Related Acute Acoustic Trauma. Journal of Special Operations Medicine. 2020; 20(4):104-111.
Magro I, Clavier O, Mojica K, Rieke C, Eisen E, Fried D, Stein-Meyers, Fellows A, Buckey J, Saunders J. Reliability of tablet-based hearing testing in Nicaraguan school children: A detailed analysis. Otology and Neurotology. 2020; 41(3):299-307.
Meinke D, Norris J, Flynn B, Clavier O. Going Wireless and Booth-less for Hearing Testing Industry. Int J Audiol. 2017; 56(SUP1):41-51.
https://www.research.va.gov/topics/hearing.cfm
https://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/interaural+attenuation
